Explain How Different Types of Rocks Are Formed From Magma
There Ive synthesized 100 years of geologic studies of magma formation into 4 short paragraphs. This mixture is usually made up of four parts.
How Are Igneous Rocks Formed Worldatlas
The formation of rocks results in three general types of rock formations.

. The chemistry of a magma determines the type of igneous rock it forms. Virtually all of the igneous rocks that we see on Earth are derived from magmas that formed from partial melting of existing rock either in the upper mantle or the crust. Olivine and pyroxene crystallize.
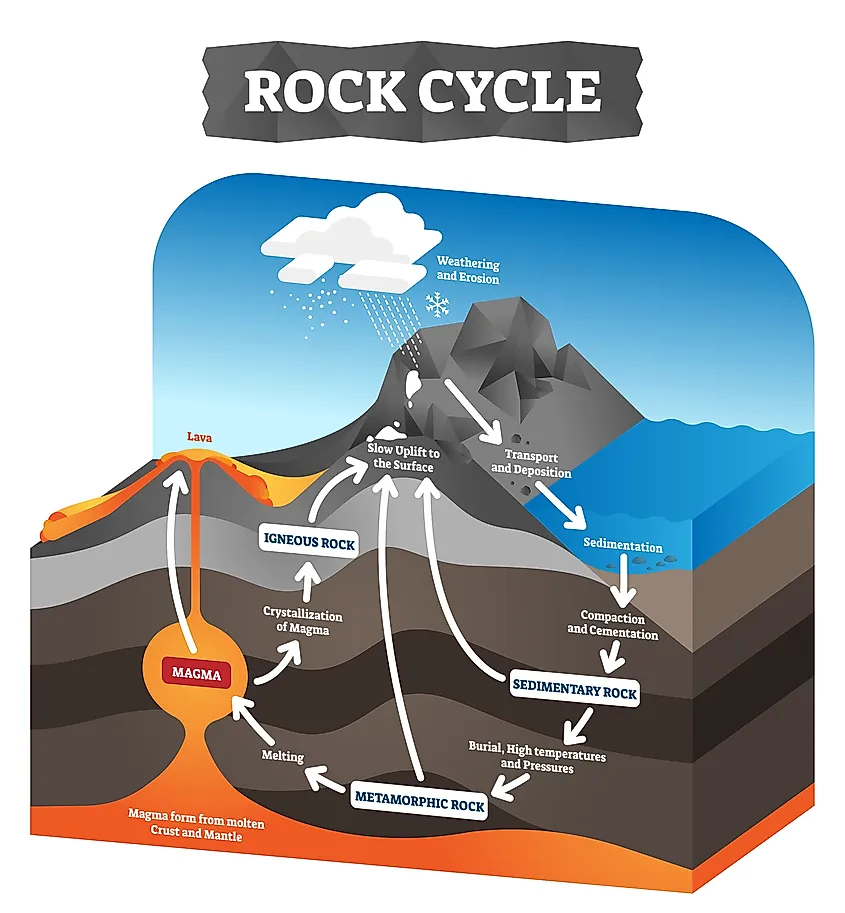
Igneous rocks form when molten rock magma or lava cools and solidifies. In this sense igneous rocks are formed when molten rock magma solidifies either underneath the earths crust to form plutonic intrusive igneous rocks or on the surface of the earth to form volcanic extrusive igneous rocks. Extrusive rocks crystallized from liquid magmas that reached the surface and were generally vented as volcanic lavas.
The heated material is the molten. They accumulate in layers. Partial melting is what happens when only some parts of a rock melt.
Magma compositions vary but will have eight main elements in different proportions. Magma Characteristics Types Sources and Evolution A magma consists mostly of liquid rock matter but may contain crystals of various minerals and may contain a gas phase that may be dissolved in the liquid or may be present as a separate gas phase. They are simply the rocks formed through heating then followed by cooling.
Sedimentary rocks form from sediments worn away from other rocks. Magma is capable of intrusion into adjacent rocks giving rise to Sills and Dikes and extrusion onto the surface as lava and explosive ejection as Tephra to form pyroclastic rocks. Mineral s crystal lized by the melt.
Different kinds of igneous rocks. Basaltic or mafic magma predominates in nonexplosive volcanic eruptions. Igneous rocks are formed from molten rock that has cooled and solidified.
Igneous rocks form when melted rock cools. Different minerals within a rocks melt at different temperatures and the amount of partial melting and the composition of the original. It is a high-temperature magma 1200 C about 2200 F characterized by flowing lava and it is made up of about 4555 percent silica SiO 2 by weight.
Plutonic intrusive igneous rock- form from the cooling of magma below the surface Volcanic extrusive igneous rock- form from the cooling of lava. Igneous rock is formed when magma which is liquid molten rock cools or sets solidifying into rock and rock formations. And dissolve d gas es.
These eight elements are also. Melted rock originates within Earth as magma. Igneous rocks form from magma intrusive igneous rocks or lava extrusive igneous rocks.
The chemical composition of a magma at the time when it cools determines the identity. The process of magma creation is referred to by geologists as magmagenesis and occurs at the upper mantle of the Earths crust due to plate tectonic effects. While cooling the magma evolves in composition because different minerals crystallize from the melt.
A hot liquid base called the melt. When magma is eject ed by a. Most rocks are made of minerals.
A magma is a body of molten rock that occurs below the surface of the earth. 71 Magma and How It Forms. Sedimentary rocks originate when particles settle out of water or air or by precipitation of minerals from water.
Solid rock s incorporate d into the melt from the surrounding confine s. The inside of the Earth is very hot - hot enough to melt rocks. One key to what makes the eruption unique is the chemical composition of the magma that feeds a volcano which determines 1 the eruption style 2 the type of volcanic cone that forms and 3 the composition of rocks that are found at the volcano.
Upon cooling from the completely molten state it is typical for silicon tetrahedra to form first and they in turn join with each other. Magma can cool to form an igneous rock either on the surface of the Earth - in which case. This occurs when magma bursts forth from the mantle or crust on to the surface.
The terminology Igneous means fire or heat. Texture is controlled by the rate of cooling. The chemistry also determines how the magma moves.
That is deceptively simple since the solidification process can be very complex. Molten rock ie magma is less dense and more buoyant than the surrounding rock as a result magma rises through Earths crust. Metamorphic rocks occur when heat andor pressure impact other rocks.
Heat transfer is the process through which a rising column of magma sends heat to the rock around it pushing it beyond melting point and creating rhyolitic magma. There are three major types of magma. Most magma is trapped in the crust but some erupts onto the Earths surface as lava.
When magma rises along a deep fault and pours out on the earths surface it is termed lava. The most abundant elements are oxygen and silicon followed by aluminum iron calcium sodium magnesium and potassium. Igneous rocks solidify from molten rock called magma within the Earth and lava on the surface.
Extrusive rocks are rocks that have formed on the surface of the earth. Metamorphic rocks result when existing rocks are changed by heat pressure or reactive fluids such as hot mineral-laden water. This material then cooled to form a variety of intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks.
Pyroxene and plagioclase crystallize. When magma cools it solidifies to form rock which is called igneous rock. At the bottom of the magma reservoir a cumulate rock forms.
In contrast the temperature of rhyolitic or felsic magma is much lower 750850 C about. They are identified by mineral content and texture the size and shape of their mineral grains. Magma that cools slowly deep in the Earth forms rock with large crystals and lava that cools quickly on the surface forms fine-grained rock.
The Tephra is all the volcanic material such as Ash Plumes Volcanic Bombs Volcanic Blocks. Magma often collects in magma chambers that may feed a volcano or turn into a pluton. There is a considerable range of melting temperaturesfor different compositions of magma.
The higher the amount.

Igneous Rock Notes Rock Cycle Igneous Rock Igneous

Infographic Rock Cycle Kids Discover Rock Cycle For Kids Rock Cycle Rock Cycle Project
Comments
Post a Comment